Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing many aspects of our lives, from healthcare and finance to transportation and entertainment. By increasing efficiency and personalizing experiences, AI is driving significant growth across industries. This guide provides an overview of the practical applications of AI and its growing impact on the future.
A world where your doctor predicts your illness before symptoms appear, your car drives you home safely while you rest, and your favorite shows and music are tailored just for you. Gone—all thanks to artificial intelligence. AI isn’t just the future. It is a powerful force that is currently changing our daily lives. Dive in to discover how this cutting-edge technology is reshaping the world as we know it.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is more than just a buzzword—it’s a revolutionary technology that’s changing the way we live, work, and interact with the world. From accurately diagnosing diseases to driving our cars and even curating our entertainment, AI is seamlessly integrating into various aspects of our daily routines. This incredible technology is enabling smart decisions, personalized experiences, and innovations that were once the stuff of science fiction.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the field of computer science devoted to creating systems capable of performing tasks that would normally require human intelligence. These tasks include understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, solving problems, and making decisions. At its core, AI aims to develop machines and software that can mimic human cognitive functions.
Key Concepts:
Definition: AI is the simulation of human intelligence in machines designed to think and learn like humans. It involves computer programming to process data, recognize patterns, and make decisions.
Types of AI:
- Narrow AI (weak AI): This type of AI is designed for a specific task or set of tasks. Examples include voice assistants such as Siri or Alexa, recommendation systems on streaming platforms, and chatbots.
- General AI (Strong AI): This is a theoretical form of AI that will have the ability to perceive, learn, and apply human-like intelligence to a wide range of tasks. General AI doesn’t exist yet.
History of AI:
- The concept of AI has been around for centuries, but the field began to take shape in the 20th century. Important milestones include the development of early computing machines, the coining of the term “artificial intelligence” at the Dartmouth conference in 1956, and the development of machine learning algorithms in recent decades.
Key Ingredients:
- Machine Learning: A subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed. It includes algorithms that identify patterns and make predictions.
- Neural Networks: Inspired by the human brain, a neural network is a series of algorithms designed to recognize patterns. They are used in a variety of applications including image and speech recognition.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): This branch of AI focuses on interactions between computers and humans using natural language. It enables machines to understand, interpret and respond to human language.
History of AI
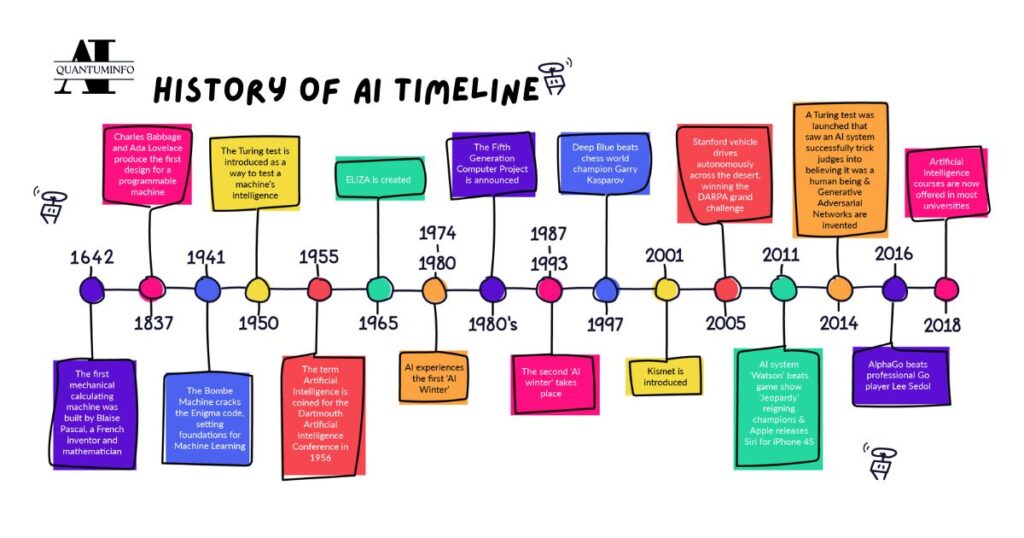
Artificial intelligence (AI) has a rich history marked by significant milestones and advances. Here is a brief overview:
Basic Concepts and Basics
- Antiquity: The idea of artificial beings with intelligence can be found in ancient myths and legends. Concepts of automata and mechanical devices that imitate human actions exist in various cultures.
- 17th-19th century: Philosophers and mathematicians, such as René Descartes and George Boll, laid the foundations of logical reasoning and computational thinking, which are essential to AI.
Birth of Modern AI
- 1950s: The modern field of AI begins to take shape. In 1950, Alan Turing proposed the Turing Test as a measure of a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior that is indistinguishable from that of a human. The term “artificial intelligence” was coined by John McCarthy at the Dartmouth Conference in 1956, which is considered the official birth of AI as a research field.
- 1950-1960: Early AI research focused on symbolic methods and problem-solving techniques. Researchers developed algorithms and programs that could perform tasks such as playing chess and solving math problems.
The Rise and Fall of AI Enthusiasm
- 1970s–1980s: The field experienced its first “AI winter,” a period of low funding and interest due to unpredictable expectations and limitations of early AI systems. However, advances in expert systems and knowledge representation continued to drive research.
- 1980s–1990s: The development of more sophisticated algorithms, along with increased computational power, led to renewed interest in AI. Expert systems, which used knowledge databases to make decisions, gained popularity in industries such as finance and healthcare.
Emergence of Machine Learning
- 1990s–2000s: AI research shifts focus to machine learning, a subset of AI that emphasizes learning from data rather than relying entirely on programmed rules. Advances in algorithms and the availability of large data sets enabled significant advances in areas such as speech recognition and image processing.
- 1997: IBM’s Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov, demonstrating AI’s prowess in strategic thinking and problem-solving.
Advanced AI and Deep Learning
- 2010-present: The rise of deep learning, a subset of machine learning that includes neural networks with many layers, has led to major advances in AI. Technologies such as autonomous vehicles, advanced language models, and sophisticated image recognition systems have emerged.
- 2016: Google’s AlphaGo defeated the world champion in the board game Go, demonstrating AI’s ability to handle complex, strategic tasks.
- 2020: AI is advancing rapidly, with applications in various fields including healthcare, finance, entertainment, and more. The development of large language models such as GPT-3 has demonstrated the ability of AI to produce human-like text and perform complex language tasks.
Getting Started with AI
Getting started with AI involves a few key steps to build a basic understanding and begin hands-on experience.
First, familiarize yourself with the basics of AI. Learn about fundamental concepts such as machine learning, neural networks, and natural language processing. Online resources, introductory courses, and books can provide a solid foundation in these areas.
Next, choose a programming language commonly used in AI development, such as Python. Python is popular due to its simplicity and extensive libraries available for AI such as TensorFlow and PyTorch.
Here, Artificial Intelligence Detection
Discover AI tools and frameworks that can help you develop AI models. These tools offer pre-built functions and structures for tasks such as data processing, model training, and evaluation. Start with beginner-friendly platforms like Google Colab or Jupyter Notebooks, which provide an interactive environment for coding and experimenting.
Work on small projects to apply what you’ve learned. Start with simple tasks like building a basic hierarchy or chatbot. These projects will help you understand how AI models are trained and tested.
Finally, keep learning and iterating. AI is a rapidly evolving field, so it is vital to stay updated with the latest developments, techniques, and tools. Participate in online communities, attend workshops, and continue experimenting to hone your skills and knowledge.
Different Types of AI
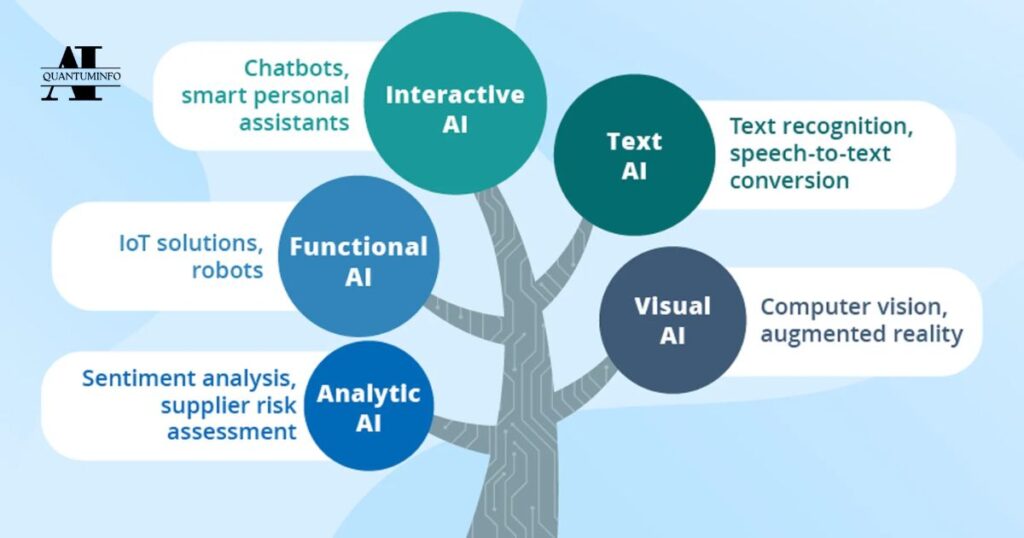
Narrow AI (Weak AI):
Narrow AI refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to handle specific tasks or solve specific problems. Unlike human intelligence, which can adapt to a variety of tasks, Narrow AI is specialized and focused. Examples:
- Virtual assistants: Tools like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa help users with things like setting reminders, answering questions, and controlling smart home devices.
- Recommender systems: Algorithms used by platforms like Netflix and Amazon to recommend movies, shows, or products based on user preferences and past behavior.
- Chatbots: Automated systems used in customer service that can answer questions, process requests, and provide assistance through text or voice interactions.
General AI (Strong AI):
- Definition: General AI, also known as Strong AI or Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), refers to a type of AI that can perceive, learn, and apply knowledge to a wide range of tasks similar to human cognitive abilities. keeps It can perform any intellectual task that a human can do.
- Status: General AI is still theoretical and not yet achieved. This represents a significant leap from current AI systems, which are specialized and limited in scope. Researchers are working towards the development of AGI, but this is a future goal rather than a current reality.
Artificial Super Intelligence:
- Definition: Artificial superintelligence is a hypothetical form of AI that will surpass human intelligence in all aspects, including creativity, problem-solving, and emotional understanding. It represents an advanced stage of AI development where the machine’s capabilities far surpass those of the best human minds.
- Status: Artificial superintelligence is a theoretical concept and is not currently achievable. It is often discussed in terms of its potential benefits and risks, and its development will raise important ethical and safety concerns.
How AI works
AI systems work by simulating certain aspects of human intelligence through a series of computational processes. The journey begins with data collection, where the AI system collects relevant information from various sources. This data can include text, images, numbers, or sensor readings, depending on the task at hand. For example, a face recognition system will collect multiple images of faces with identifying labels.
After data collection, the next step is to select an algorithm. Algorithms are a set of rules or methods that AI uses to process data and make decisions. Different types of algorithms are suitable for different tasks, such as classification, regression, or clustering. For example, a decision tree or neural network can be chosen based on the specific problem that the AI needs to solve.
Here, A Future Insight of AI Transforming Agriculture
With the selected algorithm, the AI model undergoes training. During this phase, AI learns from data by identifying patterns and making predictions. The system continuously adjusts its parameters based on errors to increase its accuracy. For example, a spam filter learns to distinguish between spam and legitimate emails by analyzing examples and fine-tuning its rules.
After training, the AI model is evaluated. This involves evaluating the performance of the model and testing it with new, unseen data to ensure it generalizes well to real-world scenarios. For example, a spam filter is tested with a fresh batch of emails to verify its effectiveness in identifying spam.
Once the model passes evaluation, it is ready for deployment. At this stage, the AI system is integrated into practical applications where it can make predictions or decisions based on new input data. For example, a spam filter becomes part of the email system to automatically filter out unwanted messages.
In some cases, AI systems engage in continuous learning. This means they process new data over time to stay updated and improve their performance. For example, a recommendation system on a streaming service adapts its recommendations based on user interactions and evolving preferences. This ongoing learning helps ensure that AI remains relevant and effective in its applications.
Practical Applications of AI

Health care
AI is transforming healthcare by improving diagnosis, treatment, and research. For example, AI systems can analyze medical images such as X-rays and MRIs to identify diseases such as cancer with high accuracy.
AI also helps predict patient outcomes and personalize treatment plans by analyzing vast amounts of health data. Additionally, AI helps drug discovery by analyzing chemical compounds and predicting their effectiveness, accelerating the development of new drugs.
Treasury
In the financial sector, AI enhances various processes. Fraud detection systems use AI to monitor transaction patterns and detect unusual activity that may indicate fraudulent behavior.
Automated trading algorithms can execute trades based on market data at high speeds, often outperforming human traders.
AI also powers robo-advisors that provide personalized financial advice and investment recommendations based on individual financial goals and risk tolerance.
Retail
AI significantly improves the retail experience for both consumers and businesses. AI algorithms recommend products based on a customer’s browsing history and previous purchases, creating a more personalized shopping experience.
Inventory management systems use AI to predict demand and optimize stock levels, reducing waste and ensuring popular items are always available. AI-powered chatbots handle customer inquiries and assist, enhancing the overall shopping experience.
Transportation
AI plays an important role in modernizing transportation. Autonomous vehicles equipped with AI technology can drive themselves by interpreting data from sensors and cameras, leading to safer and more efficient travel.
AI also helps improve traffic management by analyzing real-time traffic data and adjusting signal timings to reduce congestion. In logistics, AI improves route planning, ensures timely delivery, and reduces fuel consumption.
Entertainment
AI enhances the entertainment industry by personalizing content and improving user experiences. Streaming platforms like Netflix and Spotify use AI to recommend movies, shows, and music based on user preferences and viewing history.
AI also helps create customized playlists and discover new content that suits individual tastes. Additionally, AI is being used to produce original content including scripts and music, contributing to the creative process.
Future of AI
The future of AI is poised for transformative advances in multiple fields. A key development will be the increased automation of complex tasks. AI technologies are expected to increase productivity by automating functions, from self-driving vehicles to sophisticated supply chain management. These developments will likely lead to more efficient operations and innovation in various industries.
Another important trend is the evolution of AI models themselves. Future AI systems will be more powerful and sophisticated, with better capabilities to understand and create human-like text, recognize complex patterns, and make more critical decisions. These developments will push the limits of what AI can achieve and open up new possibilities for applications and solutions.
In the realm of healthcare, AI is poised to play an important role. This will contribute to personalized medicine by making more accurate diagnoses, tailored treatment plans, and speeding up the drug discovery process. This potential for accuracy and efficiency can significantly increase the quality and accessibility of healthcare services.
As AI becomes more integrated into everyday life, ethical and regulatory considerations will become increasingly important. Ensuring that AI systems are designed and deployed in a fair, transparent, and secure manner. This includes addressing concerns about privacy, bias, and the impact of AI on jobs and society.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does AI improve the accuracy of medical diagnosis?
AI improves diagnostic accuracy by analyzing medical images and data more accurately, often identifying conditions that the human eye might miss. It uses advanced algorithms to detect patterns and anomalies in large data sets.
What are the potential benefits of using AI in drug discovery?
AI accelerates drug discovery by predicting how different compounds interact with targets, thereby rapidly identifying promising candidates. This reduces the time and cost associated with developing new drugs.
How are automated trading algorithms different from traditional trading methods?
Automated trading algorithms execute trades based on predefined criteria and data analysis, often at high speed. In contrast, traditional trading relies on human judgment and manual decision-making.
What are the benefits of using AI for inventory management in retail?
AI improves inventory management through demand forecasting and automated stock replenishment. It reduces overstocks and stockouts, ensuring that products are available when needed.
How is AI being used to create original content in the entertainment industry?
AI produces original content by using algorithms to create scripts, music, and other media. It helps the creative process by providing new ideas and automating content creation tasks.
Final Thoughts
AI is rapidly transforming various industries by increasing efficiency, personalization, and innovation. From revolutionizing healthcare with more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatments to reshaping finance through advanced fraud detection and automated trading, the impact of AI is deep and far-reaching.
In retail, AI improves customer experiences with tailored recommendations and optimal inventory management, while in transportation, it drives safety and efficiency through autonomous vehicles and intelligent traffic management.
In entertainment, AI personalizes content and aids the creative process, offering new ways to engage audiences. As AI continues to evolve, it promises to further develop and make significant improvements in multiple domains, making it an integral component of future technological advancements.









